AG Alzheimer / Zheng
Role of activin receptor signaling in hippocampal neurophysiology, in anxiety, depression, stress and in alcohol abuse
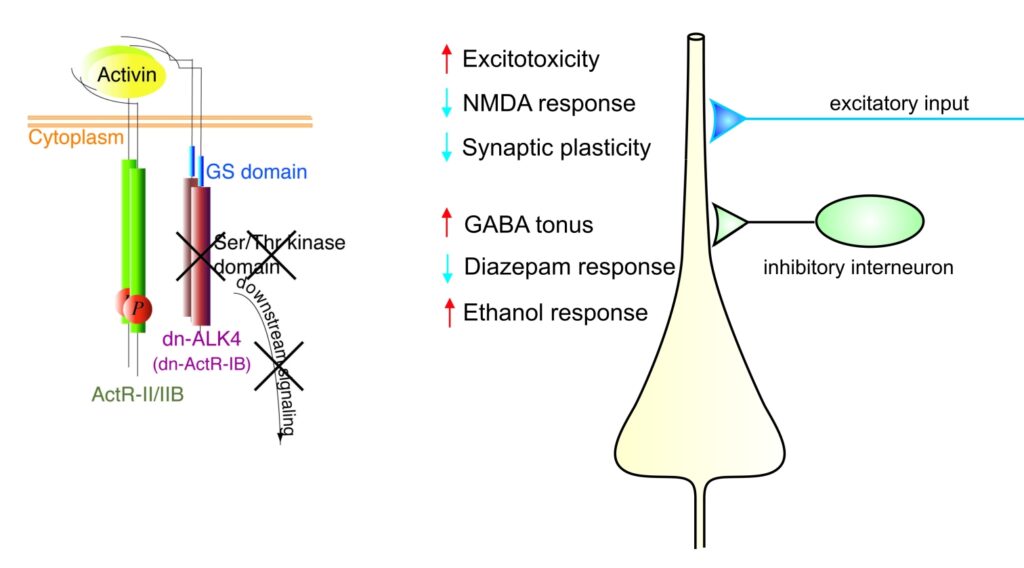
Activins belong to the transforming growth factor β (TGF β) family and are now recognized as multifunctional regulatory proteins. Whereas we and others have firmly established a neuroprotective role of activin in acute brain injury, it remained unclear whether activin also influences the operation of neuronal circuits under physiological conditions. To elucidate the functions of activin in normal adult brain, S. Werner and her group at the Institute of Molecular Health Sciences (ETH Zurich) generated transgenic mice expressing a dominant-negative mutant of activin receptor IB (dnActRIB) under the control of the CaMKIIα promoter.
We are currently exploring how activin receptor signaling tunes cellular and network properties underlying cognitive functions and affective behavior. In particular, we are examining
- how the pronounced dorsal-to-ventral gradient of activin A shapes the distinct signature properties of dorsal and ventral hippocampus.
- how the strong enhancement of activin signaling by enriched environment recalibrates hippocampal networks and affords protection against adolescent stress.
- how activin signaling influences the long-term effects of adolescent binge drinking on the adult brain.
Zheng et al., Neuroforum 2017 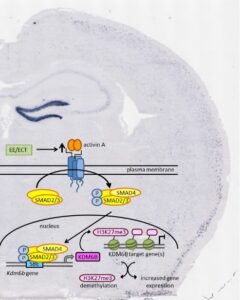
Link et al., Front Mol Neurosci, 2016 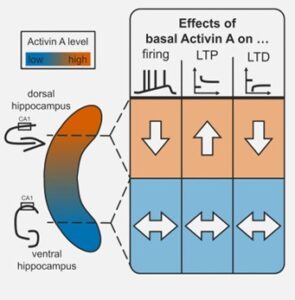
Dahlmanns et al., iScience, 2023 
Schmidt et al., Hippocampus 2022
Selected publications
- Tretter YP, Hertel M, Munz B, ten Bruggencate G, Werner S and Alzheimer C: Induction of activin A is essential for the neuroprotective action of bFGF in vivo. Nature Med 6: 812-815, 2000.
- Müller M, Zheng F, Werner S and Alzheimer C. Transgenic mice expressing dominant-negative activin receptor IB in forebrain neurons reveal novel functions of activin at glutamatergic synapses. J Biol Chem 281:29076-29084, 2006.
- Zheng F, Adelsberger H, Müller MR, Fritschy J-M, Werner S and Alzheimer C: Activin tunes GABAergic neurotransmission and modulates anxiety-like behavior. Mol Psychiatry 14:332-346, 2009.
- Krieglstein K, Zheng F, Unsicker K and Alzheimer C. More than being protective: functional roles for TGF-β/activin signaling pathways at central synapses. Trends Neurosci 34: 421-429, 2011.
- Link AS, Kurinna S, Havlicek S, Lehnert S, Reichel M, Kornhuber J, Winner B, Huth T, Zheng F, Werner S, Alzheimer C. Kdm6b and Pmepa1 as targets of bioelectrically and behaviorally induced activin A signaling. Mol Neurobiol 53:4210-4225, 2016.
- Schmidt CC, Zheng F, Alzheimer C. Activin A regulates the excitability of hippocampal mossy cells. Hippocampus 32:401-410, 2022.
- Dahlmanns M, Jana Katharina DahlmannsJK, Valero-Aracama MJ, Zheng F, AlzheimerC. Environmental enrichment recruits activin A to recalibrate neural activity in mouse hippocampus. Cerebral Cortex 33: 663-675, 2023.
- Dahlmanns M, Valero-Aracama MJ, Dahlmanns JK, Zheng F, Alzheimer C. Tonic activin signaling shapes cellular and synaptic properties of CA1 neurons mainly in dorsal hippocampus. iScience doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.108001, 2023.
- Stürzenberger S, Bülow N, Kalinichenko LS, Licha R, Eulenburg V, Dahlmanns M, Müller CP, Zheng F, Alzheimer C. Heavy adolescent drinking makes the adult brain more vulnerable to ethanol by permanently altering the age-dependent interplay between alcohol, GIRK channels and activin. Mol Psychiatry Epub ahead of print, org/10.1038/s41380-025-03210-x, 2025.
Neuropsychiatric disease models, mechanisms of drug action and cryopreservation of brain tissue
In collaboration with Christian P. Müller and Johannes Kornhuber (Dept. of Psychiatry, University Hospital Erlangen), we are exploring mechanisms of drug action in animal models of neuropsychiatric diseases.
In collaboration with Alex German (Molecular Neurology, University Hospital Erlangen), we are examining functional recovery of adult mouse hippocampus after cryopreservation by vitrification.
Selected publications
- Tischbirek CH, Wenzel EM, Zheng F, Huth T, Amato D, Trapp S, Denker A, Welzel O, Lueke K, Svetlitchny A, Rauh M, Deusser J, Schwab A, Rizzoli SO, Henkel AW, Müller CP, Alzheimer C, Kornhuber J, Groemer TW. Use-dependent inhibition of synaptic transmission by the secretion of intravesicularly accumulated antipsychotic drugs. Neuron 74:830-844, 2012.
- Groos D, Zheng F, Rauh M, Quinger B, Kornhuber J, Müller CP, Alzheimer C. Chronic antipsychotic treatment targets GIRK current suppression, loss of LTD, and behavioral sensitization in a mouse model of amphetamine psychosis. J Psychopharmacol 33: 74-85, 2019.
- Amato D, Canneva F, Cumming P, Maschauer S, Groos D, Wrosch J, Groemer T, Chiofalo L, Dahlmanns M, Zheng F, Kornhuber J, Prante O, Alzheimer C, von Hörsten S, Müller CP. A dopaminergic mechanism of antipsychotic drug efficacy, failure, and failure reversal: the role of the dopamine transporter. Mol Psychiatry 25: 2101-2118, 2020
- El Hamdaoui Y, Zheng F, Fritz N, Ye L, Anh Tran M, Schwickert K, Schirmeister T, Braeuning A, Lichtenstein D, Hellmich UA, Weikert D, Heinrich M, Treccani G, Schäfer MKE, Nowak G, Nürnberg B, Alzheimer C, Müller CP, Friedland K. Analysis of hyperforin (St. John’s wort) action at TRPC6 channel leads to the development of a new class of antidepressant drugs. Mol Psychiatry 27: 5070-5085, 2022.
- German A, Yağız Akdaş E, Flügel-Koch C, Fejtova A, Winkler J, Alzheimer C, Zheng F. Functional recovery of the adult murine hippocampus after cryopreservation by vitrification. bioRxiv, https://doi.org/10.1101/2025.01.22.634384.
Fang Zheng: Complete list of publications on ORCID
Christian Alzheimer: Complete list of publications on PubMed

Nadja Treiber
AG Alzheimer / Zheng

Paul Schmuda von Trzebiatowski
AG Alzheimer / Zheng

Sophia Stürzenberger
AG Alzheimer / Zheng

Luisa Theissen
AG Alzheimer / Zheng

